Guidelines and Principles: Governance
Effective governance ensures accountability and strategic direction.
12 Major Areas of Nonprofit Management
SEE ALSO: Ten Basic Responsibilities of Nonprofit Boards (Boardsource)
A nonprofit board of directors is responsible for defining the organization’s mission and for providing overall leadership and strategic direction to the organization. A nonprofit board actively sets policy and ensures that the organization has adequate resources to carry out its mission. The board provides direct oversight and direction for the executive director and is responsible for evaluating his/her performance. A nonprofit board also has a responsibility to evaluate its own effectiveness, in upholding the public interest(s) served by the organization.
Assessment Items
Board Composition & Roles
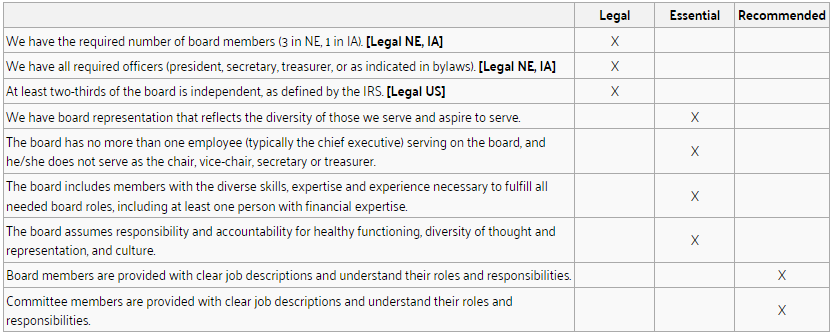
Board Independence

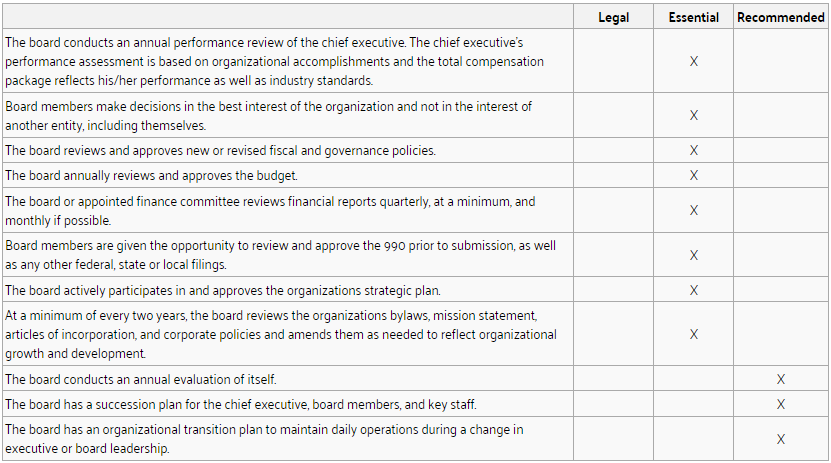
Board Oversight
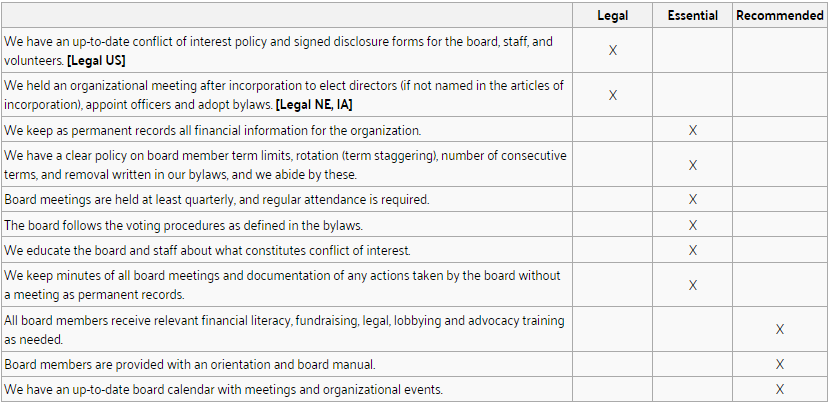
Board Policies & Procedures
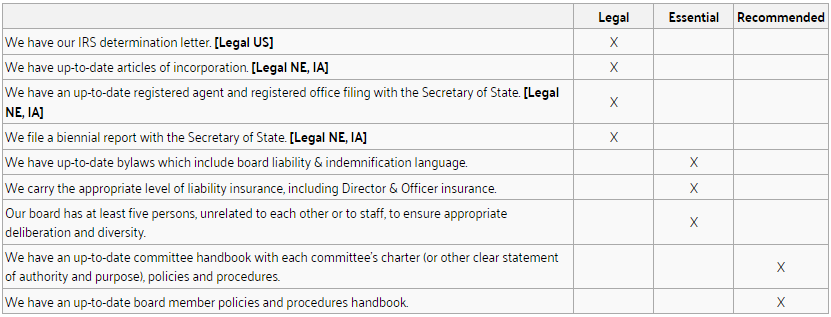
Documents
Resources
- Conflict of interest policy, procedures & signed forms for board, staff, & volunteers—updated annually (Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002; 990)
- IRS Form 1023 & IRS determination letter—publicly accessible for accountability purposes
- Articles of incorporation (Neb. Rev. Stat. §21-1921; Iowa Code §504.202)
- Establish within 60 days and continuously maintain a registered office and registered agent (Neb. Rev. Stat. §21-1934, §21-1935, §21-1937)
- File biennial report (by April 1st, in odd years) with Secretary of State (Neb. Rev. Stat. §21-125; Iowa Code §504.1613) NE, IA
- Hold an organizational meeting after incorporation to elect directors (if not named in the articles) appoint officers, adopt bylaws, and carry on other business (Neb. Rev. Stat. §21-1924; Iowa Code §504.205) NE, IA
- Required officers—president, secretary and treasurer, or as indicated in bylaws (Neb. Rev. Stat. §21-1990; Iowa Code §504.841) NE, IA
- Minimum of three board members (Neb. Rev. Stat. §21-1970) NE
- Notify NE Secretary of State if registered agent or registered office has been changed or discontinued within 120 days (Neb. Rev. Stat. §21-19,137) NE [needs research and complete reference]
- Minimum of one board member (Iowa Code §504.803) IA
- Notify IA Secretary of State if registered agent or registered office has been changed or discontinued within 60 days (Iowa Code §504.1421) IA
- Articles of incorporation must include provisions not inconsistent with law for how assets will be distributed in case of corporate dissolution (Neb. Rev. Stat. §21-1921, §21-1922; Iowa Code §504.202) NE, IA (required for IA corporations incorporated after January 1, 2005; recommended for all others)
- Board code of ethics/conduct
- Board member reimbursement/compensation policy
- Board resolutions/minutes book
- Bylaws include board liability & indemnification language
- Liability insurances (Director & Officer, general, volunteer, etc.)
- Voting procedures
- Annual report
- Board attendance policy
- Board calendar (meetings & organizational events)
- Board giving policy (100% of board members should give)
- Board member handbook—policies & procedures including, but not limited to:
- Advocacy & lobbying
- Attendance & dismissal
- Audit process & auditor selection
- Board responsibilities/expectations/job descriptions
- Board transition (term limits, recruitment, selection)
- Committees (purpose, structure, goals, activities)
- Conflict of interest policy
- Crisis communication plan
- Executive transition (emergency & planned)
- Orientation, training & evaluation
- Board member recruitment, selection, orientation, training plans
- Board terms, rotation & removal (bylaws)
- Chief executive hiring & assessment/evaluation plan
- Committee charter(s)
- Committee descriptions (purpose, structure, goals, activities, person responsible)
- Committee policy handbooks
- Compensation documentation (executive & other staff) Note: See IRS information on “rebuttable presumption” for more details on what to have.
- Disaster recovery plan
- Executive evaluation plan
- Leadership succession & transition plan (including board & staff leadership)
- Organizational chart
- Process for determining chief executive compensation
- Risk evaluation & management systems
Best Practices
Board Composition & Roles
- Review the organization’s process for recruiting and screening potential board members. Develop a script of topics to cover during an initial meeting, including the ethics and values of the organization. Provide information on the organization’s values and ethics in a written format (i.e. board manual).
- Strive for diversity on your board to bring in fresh/alternative perspectives and approaches to achieving your mission.
- Establish term limits for board members. Staggered terms should maintain at least a 50% incumbency rate to maintain continuity and organizational identity.
- Frame board orientations around the mission. Lay out specific expectations of how board members will help achieve the mission; encourage the board chair to frame all board discussions around the mission; consider a board retreat with a specific mission focus; and provide each board member with a position description developed within the context of mission achievement.
- Board members should not manage day-to-day work of the organization. Instead, they delegate that function to others and exercise credible, reasonable, and prudent oversight without personal bias in respect to the officers, agents, and employees to whom tasks are delegated.
Board Policies & Procedures
- All board members should sign a Conflict of Interest statement, which should be updated on an annual basis to reflect any new affiliations and potential points of conflict. Once signed, the organization’s leadership needs to adhere to the Conflict of Interest Policy and understand the appropriate procedure to disclose a conflict.
- To avoid potential conflict and confusion, your organization should consider a variety of operating policies beyond the bylaws. In addition to personnel policies, consider formal policies for technology use, confidentiality, conflict of interest, and customer grievance procedures.
- Establish a transition plan to prepare for an immediate change in executive director: develop a process to select an interim executive and establish a strategy and timeline for posting the position, recruiting, screening, selecting, and orienting the new executive.
- Must establish within 60 days and continuously maintain a registered office and registered agent (NE, IA), and notify the Secretary of State if registered office or agent has changed (within 120 days NE, within 60 days IA).
Board Roles and Responsibilities Defined
BoardSource Board Roles and Responsibilities
Duty of Care
The duty of care describes the level of competence that is expected of a board member, and is commonly expressed as the level of "care that an ordinarily prudent person would exercise in a like position and under similar circumstances." This means that a board member owes the duty to exercise reasonable care when he or she makes a decision as a steward of the organization.
Duty of Loyalty
The duty of loyalty is a standard of faithfulness; a board member must give undivided allegiance when making decisions affecting the organization. This means that a board member can never use information obtained as a member for personal gain, but must act in the best interests of the organization.
Duty of Obedience
The duty of obedience requires board members to be faithful to the organization's mission. They are not permitted to act in a way that is inconsistent with the central goals of the organization. A basis for this rule lies in the public's trust that the organization will manage donated funds to fulfill the organization's mission.
